AUTHOR’S NAME – Chirayu Singh Thakur, BBA LLB (Hons), Third Year.
INSTITUTION NAME – MIT WPU, School of Law, Pune.
INTRODUCTION:
In a period where organizations assume a huge part in shaping society and the climate, the idea of Corporate Social Obligation (CSR) has acquired expanding conspicuousness.[i] At this point not restricted to profit age alone, partnerships are supposed to go past their main concern and get a sense of ownership with their impact on different partners, including workers, clients, networks, and the planet. This blog investigates the fragile harmony between profit and social impact in the domain of CSR, diving into its advantages, difficulties, and possible procedures for accomplishing significant and reasonable outcomes.
Defining Corporate Social Responsibility:
Corporate Social Responsibility, frequently truncated as CSR, alludes to a business approach that incorporates moral contemplations and social worries into its central tasks. This goes past simple generosity and includes the reconciliation of mindful practices into an organization’s methodologies and dynamic cycles. The thought is to guarantee that a business works in a way that decidedly influences society and the climate, while likewise conveying monetary achievement.
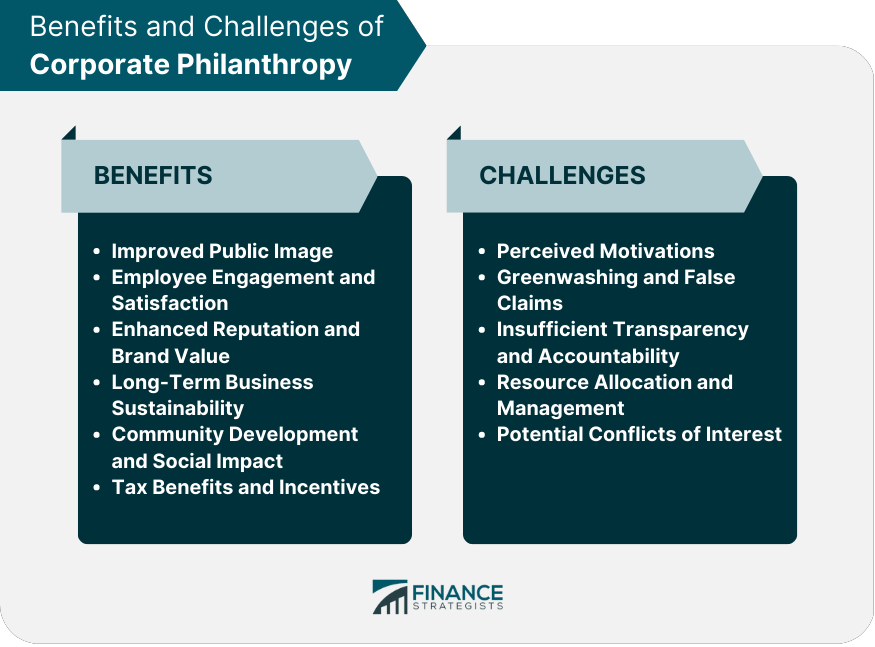
The Advantages of Embracing CSR:
- Improved Standing and Brand Picture: Participating in CSR drives can essentially upgrade an organization’s standing and brand picture. Shoppers today are more aware of the social and ecological impact of their buys, and they are bound to help organizations that line up with their qualities.[ii]
- Drawing in and Holding Ability: Organisations that focus on CSR are in many cases more appealing to expected representatives, especially among the more youthful ages who look for significant work encounters. CSR projects can likewise further develop representative spirit and fulfillment, prompting higher consistency standards.[iii]
- Risk The board: Resolving social and ecological issues through CSR can assist organizations with alleviating expected chances, like negative media inclusion or administrative punishments. By proactively resolving these issues, organizations can defend their drawn-out reasonability.
- Market Separation: CSR drives can separate an organization from its rivals by exhibiting a real obligation to social and natural causes. This separation can convert into an upper hand in the commercial center.
Challenges in Balancing Profit and Social Impact:
- Monetary Tensions: One of the essential difficulties in carrying out powerful CSR drives is the possible struggle between profitability and social impact. Designating assets to CSR endeavors can strain an organization’s monetary exhibition, particularly for more modest organizations.[iv]
- Estimation and Responsibility: Estimating the impact of CSR drives can be perplexing. Organizations need to lay out clear measurements and components to keep tabs on their development and show their responsibility to partners.
- Momentary versus Long haul Objectives: Balancing quick monetary profits with long-haul social and ecological advantages can be an interesting undertaking. Some CSR drives could set aside some margin to yield unmistakable outcomes, testing an organization’s obligation to its drawn-out vision.
- Greenwashing: The gamble of greenwashing, where an organization overstates or dishonestly guarantees its obligation to CSR, is a veritable concern. Such practices can prompt a deficiency of trust and believability among buyers and partners.
Methodologies for Powerful CSR Execution:
- Joining into Centre Business Methodology: To accomplish an agreeable harmony between profit and social impact, CSR ought to be coordinated into an organization’s central business system instead of treated as a disconnected exertion. This guarantees that capable practices become an innate piece of everyday tasks.[v]
- Partner Commitment: Drawing in with different partners, including representatives, clients, financial backers, and nearby networks, can give important experiences and viewpoints, directing the improvement of significant CSR drives.[vi]
- Laying out Clear Objectives and Measurements: Laying out distinct objectives and quantifiable measurements permits organizations to follow the advancement and impact of their CSR drives. This straightforwardness assembles believability and keeps up with center around long haul goals.[vii]
- Cooperation and Associations: Working together with different organizations, non-legislative associations, and administrative offices can intensify the impact of CSR endeavors. Pooling assets and abilities can prompt more compelling answers for complex cultural difficulties.
- Moral Administration: Solid moral authority is fundamental for driving CSR drives. At the point when pioneers focus on social and natural obligation, it establishes the vibe for the whole association and energizes a culture of responsibility.
CONCLUSION:
Corporate Social Responsibility addresses a change in perspective in the manner organizations work and collaborate with society and the climate. Finding some kind of harmony between profit and social impact is a complicated errand, yet an undertaking can yield significant advantages for organizations and the more extensive local area the same. By embracing CSR as a vital piece of their tasks, organizations have the chance to make a positive and enduring impact on society while guaranteeing their drawn-out practicality in an undeniably cognisant and interconnected world.
[i] JASON FERNANDO, Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Explained With Examples, investopedia, (Aug. 21, 2023, 7:25 PM), https://www.investopedia.com/terms/c/corp-social-responsibility.asp
[ii] CHRIS B. MURPHY, Why Social Responsibility Matters to Businesses, investopedia, (Aug. 21, 2023, 7:25 PM), https://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/041015/why-social-responsibility-important-business.asp#:~:text=What%20Are%20the%20Benefits%20of,difference%20for%20bottom%2Dline%20financials.
[iii] Id, at 03.
[iv] cyberswift, https://www.cyberswift.com/blog/csr-challenges-and-resolutions/, (last visited Aug. 16, 2023).
[v] openstax, https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/3-2-corporate-social-responsibility-and-social-entrepreneurship, (last visited Aug. 16, 2023).
[vi] panelGregor Pfajfar a, Aviv Shoham b, Agnieszka Małecka c, Maja Zalaznik d, Value of corporate social responsibility for multiple stakeholders and social impact – Relationship marketing perspective, Volume 143, Journal of Business Research, Pages 46-61, April 2022, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0148296322000613?via%3Dihub
[vii] Id, at 03.